The Definitive Guide to Managing Athlete’s Foot: Symptoms, Clinical Treatments, and Long-Term Prevention Strategies
Athlete’s foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a prevalent fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet and can easily spread to the toenails and even the hands. This condition is not exclusive to athletes; anyone who exposes their feet to damp, communal environments or fails to maintain rigorous foot hygiene can fall victim to the dermatophyte fungi that cause the infection. Understanding the biological underpinnings of this condition is the first step toward effective management. Dermatophytes are microscopic organisms that thrive in warm, moist environments, consuming keratin, a protein found in hair, skin, and nails. When these fungi find a suitable environment on the human foot, they begin to colonize the outer layers of the skin, leading to the irritation, peeling, and discomfort associated with the condition.
The transmission of athlete’s foot occurs through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungus. Common breeding grounds include locker room floors, swimming pool decks, and communal showers. Because the fungi can survive on shed skin scales for extended periods, it is remarkably easy to contract the infection simply by walking barefoot in high-traffic areas. Once the fungus takes hold, it can manifest in several different ways, ranging from mild scaling to painful, fluid-filled blisters. Addressing the infection early is critical, as untreated tinea pedis can lead to secondary bacterial infections or chronic skin issues that are much harder to eradicate.
For many individuals, the initial symptoms of athlete’s foot are ignored as simple dry skin or minor irritation. However, the persistent nature of the fungus means that it rarely disappears without targeted intervention. The skin between the toes, particularly the fourth and fifth digits, is the most common site for the infection to begin because these areas provide the perfect dark, moist environment that dermatophytes crave. As the infection progresses, it can migrate to the soles and sides of the feet, leading to a condition known as “moccasin-type” athlete’s foot. Recognizing these patterns early allows for more effective over-the-counter treatments and prevents the need for more aggressive medical interventions.
Proper diagnosis and treatment require a comprehensive understanding of how the infection interacts with the skin’s natural barrier. While most cases can be managed at home, understanding when to seek professional medical advice is paramount. This guide provides a detailed roadmap for identifying the various forms of tinea pedis, implementing clinical-grade treatment protocols, and establishing a lifestyle that prevents recurrence. By focusing on both the immediate eradication of the fungus and the long-term health of the skin, individuals can regain comfort and maintain healthy, infection-free feet throughout the year.
Detailed Symptomatology and Identification
The presentation of athlete’s foot varies significantly depending on the specific strain of fungus involved and the individual’s immune response. The most common symptom reported is persistent itching, which often intensifies immediately after removing shoes and socks. This itching is frequently accompanied by a stinging or burning sensation, particularly in the areas where the skin has begun to crack or peel. In many cases, the skin will appear red and inflamed, and in the interdigital (between the toes) variety, the skin may appear white and soggy, a process known as maceration. This occurs because the fungal infection breaks down the skin’s integrity, allowing moisture to seep into the deeper layers.
In the moccasin-type infection, the symptoms are often more subtle and may be mistaken for chronic dry skin or eczema. The skin on the soles and heels becomes thick, dry, and scaly. This scaling can extend up the sides of the feet, mimicking the shape of a moccasin shoe. Unlike the interdigital variety, this form of tinea pedis often involves both feet and is highly resistant to treatment if not addressed with potent antifungal agents. Over time, the thickened skin can develop deep, painful cracks called fissures, which serve as entry points for bacteria, potentially leading to more serious infections like cellulitis.
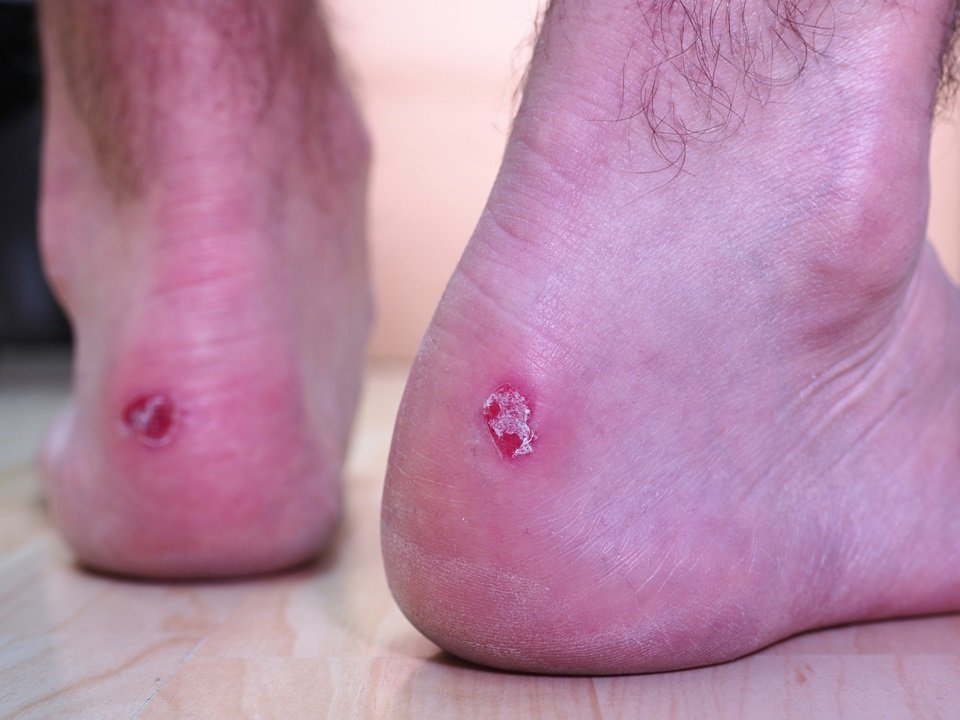
The vesiculobullous variety is the least common but often the most painful form of athlete’s foot. This type is characterized by the sudden outbreak of fluid-filled blisters, usually on the instep or the underside of the foot. These blisters are the result of an inflammatory reaction to the fungus. When the blisters burst, the skin underneath is often raw and highly sensitive. This form of the infection requires careful handling to prevent the spread of the fungal spores contained within the blister fluid and to avoid secondary infections in the open wounds.
Beyond the physical appearance of the skin, athlete’s foot can also cause a distinct, unpleasant odor. This malodor is caused by the metabolic byproducts of the fungi and any opportunistic bacteria that colonize the damaged skin. It is important to note that athlete’s foot can also spread to the toenails (onychomycosis), causing them to become thick, discolored, and brittle. Once the fungus enters the nail bed, treatment becomes significantly more complex and often requires systemic oral medications prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Classifying the Common Varieties of Tinea Pedis
Understanding the specific type of fungal infection is essential for choosing the right treatment strategy. Below are the primary classifications of athlete’s foot infections:
- Interdigital Infection: This is the most prevalent form, typically occurring between the two smallest toes. It manifests as peeling, redness, and scales, and can cause the skin to feel soft and moist due to trapped perspiration.
- Moccasin-Type Infection: This variety affects the soles, heels, and sides of the feet. It often starts with mild soreness and progresses to dry, silvery scales that cover the entire bottom of the foot, often mistaken for simple calluses.
- Vesicular Infection: Characterized by a sudden eruption of blisters, this type usually affects the arch or instep. It is often triggered by a seasonal change or high levels of foot perspiration and requires immediate antifungal intervention.
- Ulcerative Infection: This is a more severe form where the skin between the toes begins to erode, leaving open sores. It is frequently complicated by bacterial infections and is common in individuals with compromised immune systems or diabetes.
- Onychomycosis Complication: While technically a nail infection, it frequently co-occurs with athlete’s foot. The fungus spreads from the skin to the nail, leading to yellowing, thickening, and eventually the lifting of the nail from the bed.
The severity of these symptoms can be influenced by environmental factors such as the type of footwear worn and the level of physical activity. For example, athletes who wear tight, non-breathable synthetic shoes are at a much higher risk for the ulcerative and interdigital types because the lack of airflow creates a pressurized incubator for fungal growth. Conversely, individuals who walk barefoot in gym environments are more likely to pick up the initial spores that lead to the moccasin variety.
Clinical and Over-the-Counter Treatment Protocols
The treatment of athlete’s foot is centered on the use of antifungal medications that either kill the fungus (fungicidal) or inhibit its growth (fungistatic). For mild to moderate cases, over-the-counter (OTC) medications are usually the first line of defense. These products come in various forms, including creams, sprays, powders, and gels. The most effective OTC active ingredients include terbinafine, clotrimazole, miconazole, and tolnaftate. Terbinafine is often preferred because it is fungicidal and can often resolve the infection with a shorter course of treatment compared to the azole-class medications like clotrimazole, which are typically fungistatic.
Consistency is the most important factor in the success of any antifungal treatment. Many people make the mistake of stopping the medication as soon as the visible symptoms disappear. However, the fungus can remain dormant in the deeper layers of the skin. Most medical professionals recommend continuing the application for at least one to two weeks after the skin appears healed to ensure that the infection is completely eradicated. Failure to complete the full course of treatment is the leading cause of “recurrent” athlete’s foot, which is often just the original infection resurfacing.
In cases where OTC treatments fail, or if the infection is particularly widespread, a doctor may prescribe prescription-strength topical or oral medications. Prescription topicals often contain higher concentrations of antifungal agents or combine them with mild corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching more rapidly. Oral medications, such as itraconazole or fluconazole, are typically reserved for severe cases, moccasin-type infections that cover a large area, or infections that have spread to the toenails. These systemic treatments are highly effective but require monitoring by a physician due to potential side effects, including impact on liver function.
In addition to medication, specialized foot soaks can assist in the healing process. Soaking the feet in a solution of aluminum acetate (Burrow’s solution) can help dry out blisters and reduce skin maceration in interdigital infections. For the dry, scaly moccasin type, urea-based creams can be used alongside antifungal medications to help soften the thickened skin, allowing the antifungal agent to penetrate more deeply. Managing the skin’s environment during treatment is just as important as the medication itself; the feet must be kept as dry as possible to deprive the fungus of the moisture it needs to survive.
Advanced Hygiene and Prevention Strategies
Preventing the recurrence of athlete’s foot requires a multifaceted approach to hygiene that extends beyond the feet to include footwear and living environments. The primary goal of prevention is to eliminate the moisture and warmth that dermatophytes require. This begins with the selection of appropriate footwear. Shoes made of natural materials, such as leather or breathable mesh, allow for better air circulation than synthetic materials. It is also vital to rotate shoes daily, giving each pair at least 24 hours to dry out completely before being worn again. Using cedar shoe trees or antifungal sprays inside the shoes can further reduce the fungal load.
Sock selection is equally critical. Traditional cotton socks can actually be detrimental because they absorb moisture and hold it against the skin. Instead, individuals should opt for moisture-wicking synthetic blends or wool socks specifically designed to pull sweat away from the foot. Changing socks at least once a day—or more frequently if engaged in physical activity—is a fundamental practice for anyone prone to fungal infections. For those with excessively sweaty feet (hyperhidrosis), using an antiperspirant on the soles of the feet can significantly decrease the moisture available to the fungus.
Communal hygiene is the next pillar of prevention. In environments like gyms, pools, and hotels, the “always wear shoes” rule is non-negotiable. Shower shoes, flip-flops, or waterproof sandals should be worn at all times in these areas to provide a physical barrier between the skin and potentially contaminated surfaces. After bathing, the feet must be dried with extreme care. Using a dedicated “foot towel” and ensuring the areas between the toes are bone-dry is essential. Some practitioners recommend using a hairdryer on a cool setting to ensure no moisture remains between the toes before putting on socks.
Finally, maintaining the health of the skin barrier is a long-term preventive measure. Intact skin is much more resistant to fungal invasion than skin that is cracked, callused, or irritated. Regularly moisturizing the feet (while avoiding the spaces between the toes) helps keep the skin flexible and prevents the fissures that the moccasin-type fungus loves to inhabit. If you live with others, it is imperative not to share towels, linens, or footwear, as these are primary vectors for the cross-contamination of fungal spores within a household.
Step-by-Step Daily Foot Care Routine for Prevention
Establishing a rigorous daily routine is the most effective way to ensure that athlete’s foot does not return after a successful treatment. Follow these steps for optimal foot health:
- Wash Thoroughly: Clean your feet daily using a mild soap. Pay extra attention to the areas between the toes, using a washcloth to gently remove dead skin cells where fungi might hide.
- Complete Drying: After washing, pat the feet dry with a clean towel. Ensure the spaces between each toe are completely free of moisture. Consider using a separate towel just for your feet to avoid spreading any residual spores to other parts of your body.
- Apply Antifungal Powder: If you are prone to infections, apply a medicated antifungal powder to your feet and inside your shoes every morning. This helps absorb sweat and provides a continuous antifungal barrier throughout the day.
- Choose Wicking Socks: Wear socks made of materials like merino wool or synthetic fibers designed for athletes. These materials move moisture away from the skin, unlike cotton which traps it.
- Rotate Footwear: Never wear the same pair of shoes two days in a row. This allows the shoes to breathe and ensures that any fungus that may have started to grow is deprived of the moisture it needs.
- Inspect Regularly: Check your feet daily for any signs of redness, scaling, or itching. Catching a recurrence in the first day or two makes it much easier to treat with simple OTC solutions.
- Sanitize Your Environment: Regularly clean your bathroom floors and shower stalls with a disinfectant that kills fungi. Wash your socks and bath mats in hot water (at least 140 degrees Fahrenheit) to kill any lingering spores.
Complications and When to See a Professional
While athlete’s foot is often viewed as a minor nuisance, it can lead to serious health complications if left unmanaged, particularly for individuals with certain underlying health conditions. The most common complication is a secondary bacterial infection. Because the fungus causes the skin to crack and peel, it creates openings in the body’s primary defense system. Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, can enter these cracks and cause cellulitis—a deep skin infection characterized by intense redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Cellulitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading to the bloodstream or lymph nodes.
Another complication is the “id reaction” or dermatophytid reaction. This is an allergic response to the fungus that causes blisters or rashes to appear on other parts of the body, such as the hands or chest, even though the fungus itself is not present in those areas. This occurs because the immune system becomes hypersensitized to the fungal proteins. Treating the primary infection on the feet is the only way to resolve these secondary rashes. Additionally, chronic athlete’s foot can lead to the permanent thickening of the skin and a higher susceptibility to other types of infections, creating a cycle of dermatological issues.
Individuals with diabetes or peripheral vascular disease must be especially vigilant. These conditions often cause poor circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy) in the feet, meaning a person might not feel the initial itching or pain of an infection. In diabetics, even a minor fungal infection can quickly escalate into a foot ulcer that is difficult to heal and may eventually lead to the need for amputation. For these high-risk groups, any sign of foot irritation should be evaluated by a podiatrist or primary care physician immediately.
Professional intervention is also necessary if the infection has spread to the toenails. Toenail fungus is notoriously difficult to treat with topical medications alone because the nail plate protects the fungus from the medicine. A podiatrist can debride (thin out) the infected nail and prescribe oral antifungals or laser treatments that are significantly more effective. Furthermore, if you experience fever, red streaks extending from the infected area, or pus drainage, you should seek urgent medical care as these are signs that a bacterial infection has taken hold.
Pro Tips for Managing Persistent Infections
To achieve the best results in your fight against tinea pedis, consider these expert insights that go beyond standard medical advice. First, consider the role of your laundry routine. Fungal spores are surprisingly resilient and can survive standard cold-water wash cycles. To truly sanitize your socks and towels, use the hottest setting possible and a splash of bleach or a specialized laundry sanitizer. Drying items on high heat in the dryer for at least 30 minutes further ensures that no viable spores remain to reinfect you the next time you dress.
Another “pro tip” involves the use of specialized shoe sanitizers. While sprays are helpful, ultraviolet (UV) shoe sanitizers are a highly effective, non-chemical way to kill 99% of bacteria and fungi living inside your footwear. Using a UV light insert every night can drastically reduce the fungal load in your shoes, which is often the missing link for people who suffer from chronic, “unsolvable” athlete’s foot. Additionally, if you work in an environment where you must wear heavy boots, consider bringing a change of socks to work and swapping them out during your lunch break to keep your feet dry for the second half of the day.
For those interested in supplemental care, tea tree oil has been shown in some studies to have antifungal properties. While it should not replace clinical medications, applying a diluted solution of tea tree oil to the skin after the primary infection has cleared may help maintain an environment that is less hospitable to fungi. However, always perform a patch test first, as some individuals are allergic to the undiluted oil. Finally, remember that the “fungus-free” lifestyle requires consistency; treat your foot hygiene with the same level of importance as your dental hygiene to ensure long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get athlete’s foot on my hands? Yes. This is known as tinea manuum. It often occurs when someone scratches their infected feet and the fungus transfers to the hands. It typically presents as extreme dryness and scaling on the palms and is treated with the same antifungal medications used for the feet.
Is it okay to wear flip-flops all the time to prevent it? While flip-flops are great for communal showers, wearing them exclusively can cause other issues like heel pain or lack of support. Furthermore, they don’t protect your feet from environmental debris that could cause small cuts. The best approach is to wear breathable, supportive shoes and save the flip-flops for the gym or pool deck.
How long does it take for athlete’s foot to go away? With proper treatment, a mild case usually clears up in two to four weeks. However, more severe moccasin-type infections or cases that involve the nails can take several months of consistent treatment to fully resolve.
Can I use anti-itch creams like hydrocortisone? You should be very careful with hydrocortisone. While it may temporarily relieve the itching, it is a steroid that can actually suppress the local immune response and allow the fungus to grow more aggressively. Only use steroid creams if they are combined with an antifungal and prescribed by a doctor.
Does vinegar help kill the fungus? Vinegar creates an acidic environment that fungi generally dislike. While a vinegar soak (one part vinegar to two parts water) can be a helpful supportive treatment to dry out the skin and reduce odor, it is rarely powerful enough to eliminate a well-established fungal infection on its own.
Conclusion
Athlete’s foot is a persistent but manageable condition that requires a dual focus on clinical treatment and rigorous hygiene. By recognizing the specific symptoms—whether they be the classic peeling between the toes, the dry scaling of the moccasin type, or the painful blisters of the vesicular type—individuals can take swift action using effective over-the-counter or prescription medications. The key to permanent relief lies in consistency: completing the full course of antifungal treatment and transforming one’s daily habits to prioritize dry, clean feet. From selecting moisture-wicking socks to sanitizing footwear and avoiding barefoot contact in communal areas, the strategies outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive defense against dermatophyte fungi. While most cases are easily handled at home, never hesitate to seek professional medical advice if symptoms persist or if you have underlying health conditions like diabetes. With the right approach, you can eliminate the discomfort of tinea pedis and maintain healthy, resilient skin for a lifetime.
Recommended For You