Understanding Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. In MS, the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath, a protective covering of nerve fibers, leading to inflammation and subsequent damage. This disruption can result in a myriad of neurological symptoms, depending on the location and extent of the damage within the central nervous system.
The exact cause of MS remains unclear, although genetic, environmental, and viral factors are thought to play a role. Studies have indicated that individuals with a family history of MS or those who have experienced certain viral infections, like Epstein-Barr virus, may have an increased risk of developing the condition. Furthermore, lifestyle factors, such as smoking and lack of vitamin D, have also been associated with a higher susceptibility to MS.
Symptoms of MS vary widely among individuals and can fluctuate over time. Common manifestations include fatigue, difficulty with coordination and balance, visual disturbances, and cognitive changes such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can either be temporary, known as relapses, or persistent, known as progressive MS. The unpredictable nature of these symptoms can significantly impact daily life and overall quality of living for those affected.
Early diagnosis of MS is crucial, as it can lead to more effective management strategies and potentially improve treatment outcomes. Recognizing the initial signs and symptoms can facilitate timely medical intervention, which is essential in slowing disease progression and enhancing the individual’s quality of life. Comprehensive assessments and diagnostic tests are key in confirming the presence of MS, assisting in planning appropriate treatment approaches tailored to that individual’s condition.
The Diagnostic Journey: Where to Start
If an individual suspects that they may be experiencing symptoms related to multiple sclerosis (MS), the first and most crucial step is to consult a healthcare professional. Early medical intervention can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and potentially slowing disease progression. It is essential to engage a primary care physician who can evaluate symptoms, perform initial assessments, and provide referrals to specialists as necessary.
During the consultation, individuals should be prepared to discuss their symptoms in detail. Common symptoms that may prompt suspicion of MS include fatigue, vision problems, motor skill difficulties, and sensory changes. A thorough symptom history will allow the healthcare professional to consider the overall clinical picture. Following this, the physician may refer the patient to a neurologist, a specialist who focuses on the assessment and treatment of neurological disorders, including MS.
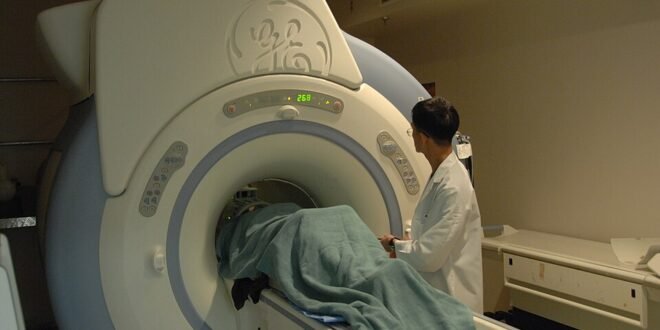
Neurologists are instrumental in the diagnostic journey as they possess the expertise to conduct more specialized tests and evaluations. They may employ various diagnostic tools, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), lumbar punctures, and evoked potentials, to assess brain and spinal cord health. These tests are critical for confirming the presence of lesions consistent with MS and ruling out other potential conditions that may mimic its symptoms.
Ultimately, the early consultation of healthcare professionals, particularly neurologists, facilitates a timely and accurate diagnosis. This step sets the stage for a comprehensive approach to treatment and management of the condition, significantly enhancing the quality of life for those affected. The journey of diagnosing MS is complex and necessitates collaboration between patients and their healthcare teams.
Medical History and Physical Examination
When considering how is MS diagnosed, the initial process typically begins with an extensive review of the patient’s medical history. Healthcare professionals focus on the patient’s symptoms, any prior health issues, family history of neurological disorders, and any incidents that could relate to the onset of multiple sclerosis. This systematic approach allows doctors to create a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health, which is crucial for determining the potential presence of MS.
During this phase, neurologists or other healthcare providers will inquire about specific symptoms that the patient may be experiencing. These symptoms can include fatigue, vision problems, muscle weakness, and difficulties with coordination or balance. Additionally, the clinician will delve into the duration and progression of these symptoms. The pattern of symptom fluctuation over time can be indicative of multiple sclerosis, as it often presents in episodes or relapses.
After the medical history has been thoroughly assessed, the next step in evaluating how is MS diagnosed involves a physical examination. This examination focuses on neurological functioning and encompasses various assessments, such as checking reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, and sensory perception. During the physical exam, doctors are particularly observant for signs of neurological deficits that may suggest MS.
The results gleaned from both the medical history and physical examination serve as foundational components in the diagnostic process. They help to exclude other possible conditions that may mimic the symptoms of multiple sclerosis, thereby aiding in delivering an accurate diagnosis. By ensuring a meticulous and detailed approach to these preliminary assessments, physicians enhance the probability of diagnosing MS accurately and effectively.
Neurological Examination: What to Expect
The neurological examination is a fundamental component in the diagnostic process for multiple sclerosis (MS). This examination provides critical insights into an individual’s nervous system functioning, and it is typically conducted by a neurologist or a trained healthcare professional. Understanding how is MS diagnosed through a neurological examination involves several standard tests and assessments aimed at evaluating both cognitive and physical health.
During the examination, a healthcare provider will assess various functions of the nervous system. One of the primary components is the assessment of reflexes. The professional may use a reflex hammer to evaluate the patient’s knee-jerk response, which helps in identifying any anomalies in the nervous system. Diminished or exaggerated reflexes can provide valuable clues as to the presence of neurological conditions, including MS.
Coordination tests are also essential in the neurological examination. Patients may be asked to perform simple tasks such as touching their finger to their nose or rapidly alternating movements. These tasks help in evaluating motor control, coordination, and balance, which are often affected in individuals with MS. The healthcare provider will carefully observe these movements to determine any coordination issues that may indicate neurological dysfunction.
Furthermore, vision assessments form a critical part of the neurological evaluation. Since multiple sclerosis can impact optic nerves, the examiner may perform tests to assess visual acuity, field of vision, and responsiveness to light. These tests are vital as they help in identifying any ocular symptoms that may be related to MS.
In conclusion, the neurological examination is a comprehensive approach in determining how is MS diagnosed, involving a series of tests to evaluate reflexes, coordination, and visual capabilities. These assessments play a pivotal role in forming an accurate diagnosis and guiding further management for those experiencing symptoms indicative of multiple sclerosis.
Diagnostic Tests for Multiple Sclerosis
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS) can be challenging due to its diverse symptoms and the absence of a single definitive test. Consequently, healthcare providers employ a variety of diagnostic tests to assess and evaluate the condition thoroughly. Among the most common methods are MRI scans, lumbar punctures, and evoked potentials, each serving a unique purpose in the diagnostic process.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a critical tool in determining the presence of MS. It produces detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, enabling the detection of lesions caused by MS. These lesions, or plaques, are indicative of damage to the myelin sheath, which protects nerve fibers. The results of an MRI can provide considerable insight into the condition’s progression and help differentiate MS from other neurological disorders. In many cases, MRI findings can substantially support the diagnosis of MS, especially when corroborated with clinical symptoms.
Another important diagnostic test is the lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap. During this procedure, a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is extracted from the spinal column. Analysis of the CSF can reveal abnormalities associated with MS, such as elevated levels of certain proteins or the presence of oligoclonal bands. These indicators strengthen the likelihood of an MS diagnosis and help exclude other possible conditions. Lumbar punctures are particularly valuable in cases where MRI results are inconclusive.
Evoked potentials are electrical tests measuring the brain’s response to sensory stimuli. These tests can evaluate how well electrical signals travel along the nerves. Delays or abnormalities in these responses may suggest demyelination, consistent with MS. By combining the results from MRI, lumbar puncture, and evoked potentials, clinicians can build a comprehensive picture of the patient’s neurological health, ultimately leading to an accurate diagnosis of multiple sclerosis.
Differential Diagnosis: Ruling Out Other Conditions
The process of diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS) is complex, primarily due to the existence of other medical conditions that may present with similar symptoms. A differential diagnosis is crucial, as healthcare providers must carefully evaluate and rule out these alternative conditions to confirm a diagnosis of MS. Symptoms frequently associated with MS include fatigue, vision problems, cognitive changes, and motor impairment, all of which can resemble various neurological or autoimmune disorders.
Common conditions that may mimic the symptoms of MS include neuromyelitis optica (NMO), transverse myelitis, and even some vitamin deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 deficiency. Additionally, diseases such as Lyme disease, lupus, and certain types of infections can exhibit overlapping symptoms, which necessitates comprehensive diagnostic procedures. A diligent healthcare provider will typically begin by reviewing the patient’s medical history and conducting a thorough neurological examination, followed by advanced imaging studies and laboratory tests.
Diagnostic imaging, particularly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), plays a vital role in the differentiation process. MRIs can reveal the presence of lesions in the central nervous system, a hallmark of MS. However, identifying lesions alone is not sufficient for a definitive diagnosis. Therefore, clinicians often employ specific diagnostic criteria, such as the McDonald criteria, which consider the presence of lesions, the history of symptom episodes, and the results of cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Moreover, ancillary tests, including blood tests and evoked potentials, may also be utilized to exclude other possible diagnoses. Evoked potentials assess the electrical activity in the brain in response to stimuli, helping to determine if there is nerve damage indicative of MS. This comprehensive approach ensures that diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is accurate and that patients receive appropriate treatment. Understanding how is MS diagnosed requires recognizing that it is an exclusionary process, underscoring the importance of ruling out other conditions that could mimic its symptoms.
The Role of Advanced Technologies in MS Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) has evolved significantly over recent years due to advancements in medical technology. These innovations are instrumental in addressing the complexities associated with how MS is diagnosed, leading to improved accuracy and efficiency in the diagnostic process.
One notable advancement is the utilization of imaging techniques, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRIs play a crucial role in visualizing brain lesions characteristic of MS. The capacity to produce detailed images of the central nervous system allows healthcare professionals to identify areas of abnormality, thus assisting in determining whether a patient meets the criteria for an MS diagnosis. Furthermore, the advent of advanced MRI techniques, including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetization transfer imaging (MTI), enhances the sensitivity of detecting subtle neurological changes that may not be visible through conventional MRI methods.
Another innovative approach in the field of MS diagnosis is genetic testing. While no single gene determines the likelihood of developing MS, research indicates that a combination of genetic factors may influence susceptibility to the disease. Genetic profiling can provide valuable insights that help clinicians assess a patient’s risk based on familial patterns. Although genetic testing alone cannot confirm a diagnosis, it aids healthcare providers in understanding individual patient profiles, potentially guiding early intervention strategies.
The incorporation of these advanced technologies not only streamlines the process of diagnosing MS but also lays the groundwork for future research. As scientists continue to explore novel approaches to understanding the disease, the integration of advanced diagnostic tools promises to enhance our capacity to accurately diagnose MS, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Consulting with Experts and Second Opinions
When navigating the complex process of how is multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosed, consulting with experts in neurology plays a significant role. The initial diagnosis can often be challenging due to the overlapping symptoms with other medical conditions. Therefore, obtaining a second opinion or consulting with additional specialists can provide clarity and reassurance for both patients and their families.
It is advisable for patients to seek a second opinion when they have doubts about their initial diagnosis or treatment options. This is particularly crucial when the diagnosis was made based on limited testing or subjective symptoms. Consulting another neurologist who specializes in MS can help ensure a comprehensive evaluation is performed. Different neurologists may have varying experiences or expertise, which can lead to new insights and recommendations that may not have been considered previously.
Patients should prepare for an additional consultation by gathering all relevant medical records, including imaging studies like MRI scans, laboratory test results, and details of any previous treatments. This information will help the new specialist conduct a thorough review and make informed recommendations regarding how MS is diagnosed and managed. Moreover, it is essential for patients to feel comfortable discussing their symptoms openly with the new neurologist, as this dialogue can significantly influence the diagnostic process.
In situations where a diagnosis remains uncertain, it may be beneficial for patients to seek further consultations with experts in specific areas such as neuro-immunology, which focuses on diseases of the nervous system, or even to interdisciplinary centers specializing in multiple sclerosis. These specialists can provide advanced testing and emergent diagnostic techniques, leading to a more accurate understanding of the patient’s condition.
Through a commitment to thorough exploration and collaboration with multiple experts, individuals can ensure that they receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan for multiple sclerosis.
Frequently Asked Questions about MS Diagnosis
The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) is often a subject of inquiry, given the complexity and variability of the condition. One of the most common questions is: how long does the diagnosis process take? The timeline for obtaining a definitive diagnosis can vary significantly among individuals. Typically, it may take several weeks to months as doctors perform a series of tests, including MRIs, neurological examinations, and possibly lumbar punctures. These steps are crucial to rule out other conditions that may present similar symptoms, ensuring that a precise diagnosis is established.
Another prevalent concern involves the next steps following a diagnosis of MS. Upon receiving a diagnosis, it is essential for patients to engage in careful discussions with their healthcare providers. Understanding the nature of MS, its potential symptoms, and the available treatment options is vital. Patients should consider joining support groups and educational resources to navigate their new circumstances effectively, as these can offer valuable insights and emotional support.
Moreover, many individuals inquire about the implications of being diagnosed with MS on their lifestyle and treatment plans. A diagnosis can initially seem overwhelming, but it does not necessarily impede the ability to live a fulfilling life. Many treatment regimens are available that can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. It is crucial for patients to maintain open communication with their healthcare team to tailor a treatment plan that aligns with their specific needs and lifestyle choices.
As people adjust to their diagnosis, they often seek out answers regarding lifestyle modifications. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress through mindfulness practices can significantly contribute to overall well-being. Understanding how is MS diagnosed and its implications can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their health.